
Good morning! Thank you for sharing a part of your day with us as we bring you the latest news and developments in AI. Let’s jump in! 📰
Today’s Menu
Appetizer: AI gives feeling to paralyzed man 🙏
Entrée: Google revolutionizes robot training 🦾
Dessert: AI recovers “extinct” antibiotics 😷
🔨 AI TOOLS OF THE DAY
👨💻 OppenheimerGPT: Use both ChatGPT and Bard in a single MacOS app! → check it out
💸 Heylibby.ai: An AI solution for lead qualification and scheduling, providing a user-friendly and efficient way to interact with leads, gather important information, and schedule meetings. → check it out
📹 Eightify: Get 8 key points from any YouTube video with this AI-powered Chrome extension. → check it out
AI GIVES FEELING TO PARALYZED MAN 🙏
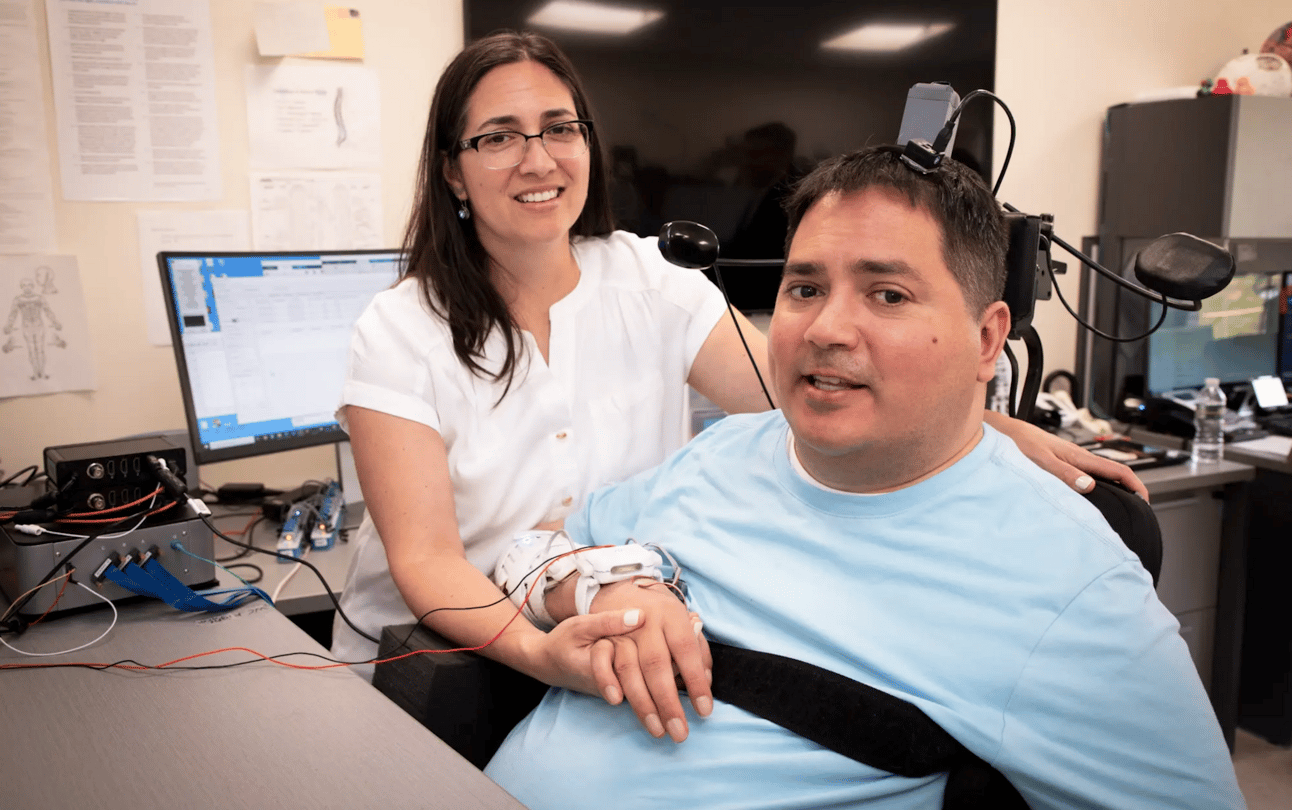

Northwell Health: Thomas holding his sister’s hand and feeling her touch for the first time in 3 years
The powers of AI are expanding beyond our wildest imaginations! This time, it is performing medical miracles. 🏥
What happened? A man named Thomas from New York was paralyzed for three years after an accident at a pool which damaged his neck and spine. After a machine learning-based surgery, Thomas now has feeling for the first time since the incident.
How did this happen? This surgery successfully “connected a computer to his brain” through microelectrode implants. Thomas was required to be awake to communicate through this 15-hour procedure.
What does this mean? Chad Bouton, a professor at Feinstein’s Institute of Bioelectronic Medicine, said, “This is the first time a paralyzed person is regaining movement and sensation by having their brain, body and spinal cord electronically linked together … We could continue to help millions of folks around the world and maybe with an even broader range of conditions.”
GOOGLE REVOLUTIONIZES ROBOT TRAINING 🦾

DeepMind: A picture of Google’s RT-2 conducting trials
Q: Why do robots make bad teachers?
A: They just drone on and on! 👨🏫
What’s new? Google has introduced the "Robotic Transformer 2" (RT-2), an AI language model with the potential to transform human-robot interaction. The RT-2 is designed to learn from both textual and visual inputs to assist and facilitate robotic actions.
How does it work? The RT-2 operates according to high-capacity vision-language models (VLMs) which are trained on web-scale datasets, combining deep learning with reinforced training techniques. By analyzing vast datasets containing diverse human interactions, it learns to decipher context, nuances, and emotional cues within language. RT-2 leverages this information to identify patterns and execute actions, even when the robot has not received explicit training for those tasks, a concept referred to as generalization. This empowers robots to not only respond accurately to direct commands but also engage in dynamic and coherent conversations with humans. RT-2 is not perfect, but performed 30% more successfully in trails than the previous model.
What does this mean? The unveiling of RT-2 is a progressive step for the marriage of AI and robotics, which implies the possibility of more sophisticated robot employment. Vincent Vanhoucke, the head of robotics at Google DeepMind, said, “Not only does RT-2 show how advances in AI are cascading rapidly into robotics, it shows enormous promise for more general-purpose robots. While there is still a tremendous amount of work to be done to enable helpful robots in human-centered environments, RT-2 shows us an exciting future for robotics just within grasp.”
AI RECOVERS “EXTINCT” ANTIBIOTICS 😷

Q: What do they call a caveman who doesn’t know where he’s walking?
A: A Meander-thal 🚶♀️
What’s up? Bioengineers have used AI to revive molecules from extinction. This groundbreaking technique, known as molecular “de-extinction,” aims to combat the growing threat of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and fuel drug development for human infections.
How did this happen? Researchers delved into the genetic data of modern humans and their ancestors—Neanderthals and Denisovans—seeking peptides with antimicrobial properties. These short protein subunits could help unlock new antibiotics, as traditional antibiotic development has slowed while antibiotic-resistant bacteria continue to wreak havoc. Using an AI algorithm, the team swiftly identified potential peptide candidates from the ancient genetic sequences. Testing the molecules in laboratory dishes and on infected mice, they discovered several potent peptides.
What does this mean? While this process is still in its early stages, the ability to bring back molecules from the past could revolutionize antibiotic development and potentially address the impending crisis of antibiotic resistance.
MONDAY MEMES 🤣



HAS AI REACHED SINGULARITY? CHECK OUT THE FRY METER BELOW
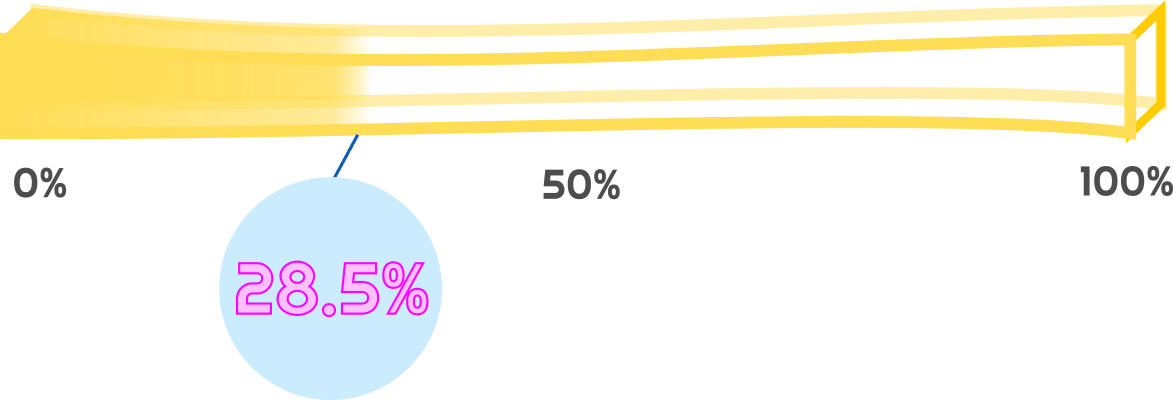
The Fry Singularity Meter ticks up slightly by 0.2%. — Not much regulation, but the AI Tools continue to flow.